Marco Navarro asks about break-in oil on our Facebook page, with attention paid to powersports engines. Thanks for the question, Marco.
Let’s get to it.
Maintaining an engine is a constant fight against wear. Over time, wear not only results in expensive damage, it reduces compression, robbing your engine of power.
That’s why it can be tough to accept that “controlled wear” during a new or rebuilt engine’s break-in period is critical to maximizing its power and longevity.
What is break-in oil?
Break-in oil is specifically formulated to seal the piston rings against the cylinder wall for maximum engine compression and power. Break-in oils use conventional base oils without friction-modifier additives to allow controlled wear between the rings and cylinder wall.
They also contain zinc and phosphorus additives to protect the camshaft and other components during break in.
How is break-in oil different from regular oil?
Break-in oil is different from regular motor oil because, by design, it is supposed to allow the rings to wear down the peaks on the cylinder wall to form a good seal. Regular motor oil, in contrast, is designed to prevent wear.
Why use break-in oil?
Let’s take a deeper dive into the idea of “controlled wear.”
Sealing the piston rings when breaking in an engine requires allowing the rings and piston skirt to carefully wear down the peaks (called asperities) on the cylinder wall.
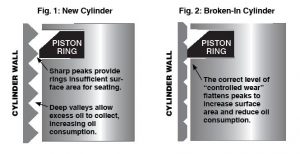
The images show what we mean.
Although a new or freshly honed cylinder appears smooth to the naked eye, it contains microscopic peaks and valleys. If the valleys are too deep, they collect excess oil, which burns during combustion and leads to oil consumption.
The sharp peaks, meanwhile, provide insufficient area to allow the rings to seat tightly. That means highly pressurized combustion gases can blow past the rings and into the crankcase, contaminating the oil and taking potential horsepower with it.
“Controlled wear” helps flatten the cylinder-wall asperities, providing increased surface area for the rings to seat tightly. The result is maximum compression (i.e. power) and minimum oil consumption.
Find out why championship engine builder Jesse Prather requires his customers to use AMSOIL Break-In Oil in his engines.
Camshaft break in
That brings us to another reason to break-in an engine: to season, or harden, the flat-tappet cam.
Flat-tappet cams can wear out faster than their roller-cam cousins, especially in engines modified with high-tension valve springs.
Worn lobes or tappets affect valve lift and duration, which reduces engine power and efficiency.
In extreme cases, increased pressure can remove material from the lobes and deposit it in the oil, where it circulates through the engine and causes damage. Using break-in oil helps harden the camshaft so it’s more resilient to wear.
That raises a critical question: How do we simultaneously allow controlled wear to the cylinder wall/piston rings while protecting the cam against wear?
Those two tasks seem mutually exclusive.
ZDDP protects the camshaft
The solution is to use a properly formulated break-in oil that contains conventional base oils and high-quality ZDDP additives.
Compared to their higher-quality synthetic counterparts, conventional base oils result in a thinner, less durable protective oil film on engine parts. The thinner fluid film allows controlled wear at the cylinder wall/ring interface.
What about the cam? Won’t it wear, too?
That’s where the additives come into play. Zinc and phosphorus anti-wear additives (usually referred to as ZDDP) are heat-activated, meaning they provide wear protection in areas of increased friction. In this case, it’s at the cam lobe/tappet interface.
The additives form a sacrificial layer on the surface of parts, which absorbs contact and helps prevent cam and tappet wear.
As a rule of thumb, a good break-in oil should contain at least 1,000 ppm ZDDP. At AMSOIL, we take it a few steps further; our Break-In Oil contains 2,200 ppm zinc and 2,000 ppm phosphorus.
When do I use break-in oil?
New cars and trucks don’t need break-in oil. The manufacturer will typically require you to drive under light-to-moderate load for a few hundred miles, then change oil. After that, you’re good to go.
Racers, competitors or gearheads using a rebuilt or new crate engine, however, should use break-in oil. Follow the engine builder’s directions or the instructions that came with the crate engine.
How long to run break-in oil?
Another rule of thumb states you should season a flat-tappet cam by running the engine above 2,500 rpm for 15 minutes.
As for seating the rings, our testing has shown it can take as few as seven dyno passes. That time varies depending on the engine, ring tension, cylinder hone and other factors.
Engine builder Jesse Prather used to run an engine 2-3 hours on the dyno to seat the rings…if they seated at all. Using AMSOIL Break-In Oil reduced that time to just 10-15 minutes.
If you don’t have access to a dyno, follow the engine builder’s or manufacturer’s recommendations. If none are provided, consult the recommendations on the break-in oil label.
In general, run the engine under light-to-moderate loads for about 500 miles. Again, that duration is a rule of thumb, but break in shouldn’t exceed 1,000 miles.
Then, drain the break-in oil, install the synthetic oil of your choice and commence driving.
An engine dyno provides the best method of determining exactly when the rings are seated. You’ll notice a boost in horsepower as the rings seat. Eventually, horsepower will stabilize once the rings are seated.
Check out 5 Ways to Boost Horsepower for Under $500.
You can also perform a leak-down test.
Another, albeit more time-consuming, method to determine if the rings are seated is to remove the exhaust headers and check for oil residue in the exhaust ports.
Presence of oil shows that the engine is burning oil, meaning the rings aren’t completely seated. Once the oil residue is gone, the rings are seated.

What about breaking in powersports engines?
Ask yourself a few questions about your motorcycle, ATV or other powersports application before using a break-in oil:
- Does it have a wet clutch? If so, the break-in oil may not be formulated for wet-clutch compatibility, leading to reduced performance.
- Does it use a shared sump with the transmission? Many motorcycles use one oil to lubricate the engine, transmission and primary chaincase. The churning action of transmission gears, especially in high-rpm applications, can tear apart – or shear – the oil if it’s not formulated to handle the stress. Using a break-in oil not designed to handle high-shear applications can lead to damage.
- Does it have a dry sump? Some motorcycles store motor oil in a tank separate from the engine. Residual break-in oil can collect in the system following the break-in period and contaminate the service-fill oil. In this case, run the engine long enough to circulate the oil throughout the system and change it a second time to ensure the break-in oil is completely removed.
Given the above challenges, we recommend breaking in a rebuilt powersports engine using the motor oil you’ve always used.
Run it according to the original equipment manufacturer’s (OEM) new-engine recommendation, then change the oil. In short, treat it like a new engine from the factory.
For new engines, just follow the OEM guidelines.
Typically they recommend a shorter interval for the first oil change to remove wear particles and contaminants from the factory. Then, change to the AMSOIL synthetic motor oil that’s recommended for your application and commence riding.
Originally published Sept. 25, 2017.







Comments
Share: